Abstract
Background: The outcomes of patients (pts) with R/R B-ALL) are poor. INO is a CD22-monoclonal antibody bound to a toxin, calicheamicin. INO has single-agent activity in R/R ALL with an 80% response rate and median survival of 7.7 months. Adding INO to low-intensity chemotherapy might further improve outcomes.
Methods: This is an open-label phase II trial designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of INO with reduced-intensity chemotherapy in R/R ALL. Pts of all ages with Philadelphia chromosome-negative pre-B ALL were eligible. Chemotherapy was of lower intensity than standard hyper-CVAD and referred to as mini-hyper-CVD (cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone at 50% dose reduction, no anthracyclines, methotrexate at 75% dose reduction, cytarabine at 0.5 g/m2 x 4 doses). Pts received mini-hyper-CVD for 8 cycles. Rituximab (if CD20+) and intrathecal chemotherapy were given for first 4 courses. INO was given on day 3 of each of the first 4 courses at a dose of 1.8 mg/m2 for cycle 1 then 1.3 mg/m2 for subsequent cycles. After the occurrence of veno-occlusive disease (VOD), INO was modified to 1.3 mg/m2 for cycle 1 followed by 1.0 mg/m2 for subsequent cycles for pts 47 and onwards. Maintenance therapy was given for 3 years with monthly vincristine at 2 mg and prednisone 50 mg daily x 5 days every monthly x 1 year, and 6-MP 50 mg bid and methotrexate 10 mg/m2 weekly x 3 years (POMP regimen).The primary efficacy outcomes included overall response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS).
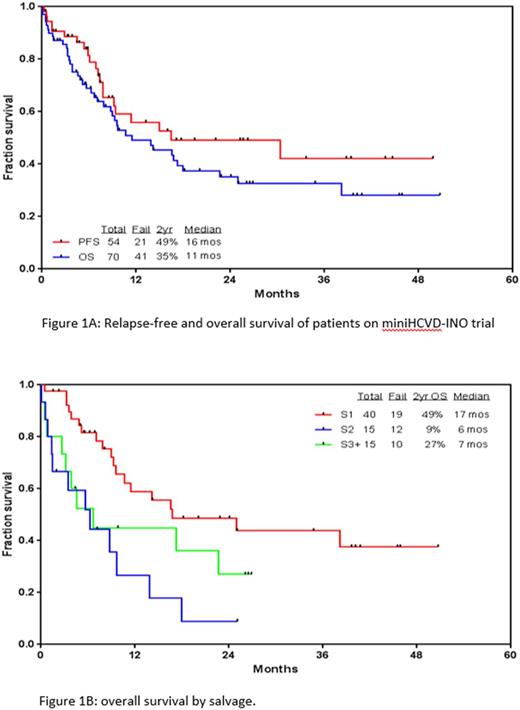
Results: Seventy pts with a median age of 35 years (range, 9-87) were treated. Overall, 54 pts (77%) responded with 41 of them (59% overall) achieving complete response (CR). 81% of responders achieved negative minimal residual disease (MRD) by 6-color multiparameter flow cytometry. Twenty-seven pts (38%) underwent subsequent allogeneic stem cell transplant (ASCT) after a median of 3 months (range, 2-8). The ORR and CR rates for pts in salvage (S) 1 were 93% and 89%, respectively. With a median follow-up of 20 months, the median relapse-free survival (RFS) and OS were 16 and 11 months, respectively. The 2-year RFS and OS rates were 49% and 35%, respectively. The 2-year rates OS for pts treated in S1, S2, and S3 and beyond were 49%, 9%, and 27%, respectively (p=0.005). Grade 3-4 toxicities included prolonged thrombocytopenia beyond 6 weeks (79%), infections during induction and consolidations (52% and 71%, respectively), hyperbilirubinemia (13%), transaminitis (11%) and veno-occlusive disease (VOD; 4%). All pts who developed VOD received ASCT (either before or after mini-hyper-CVD plus INO). When compared to a propensity matched historical cohort of pts who received INO alone (n=84), OS was significantly improved with mini-hyper-CVD plus INO (9 vs 6 months p=0.02).
Conclusions: The combination of mini-hyper-CVD and INO is safe and effective in R/R ALL pats, with a 77% ORR. Outcomes appear superior compared to INO alone in a similar population. VOD risk should be considered carefully for transplant candidates and pts with previous liver damage. Clinical trial information: NCT01371630.
Kantarjian: Novartis: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding. Thomas: Pfizer: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Cortes: BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding. Jain: Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Verastem: Research Funding; Novimmune: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Takahashi: Symbio Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. O'Brien: Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; CLL Global Research Foundation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Alexion: Consultancy; Vaniam Group LLC: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; ProNAI: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Aptose Biosciences, Inc.: Consultancy; Acerta: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Regeneron: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal